Overview:
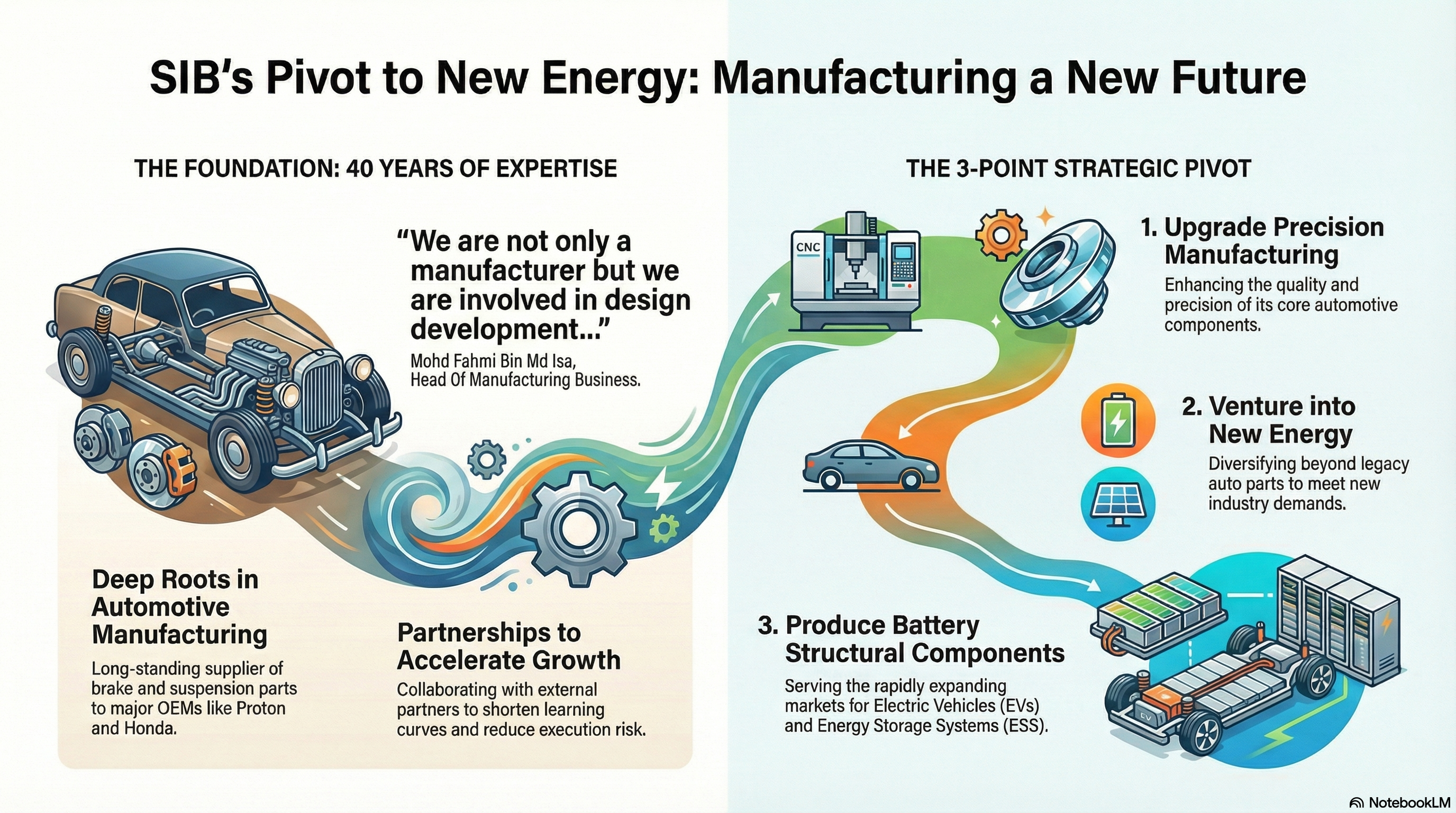
- Sapura Industrial Berhad (SIB) has been a key player in the Malaysian automotive industry for 40 years, producing metal components like brake discs, drums, and coil springs.
- The company is enhancing its capabilities to deliver more precise automotive components while venturing into new energy sectors.
- SIB is now manufacturing battery structural components for electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
- Its competitive advantage lies in decades of expertise in design and development, coupled with strategic collaborations to adopt new technologies.
- The initiative aims to drive revenue growth, build local capabilities, and support Malaysia’s role in the global new energy industry aligned with ESG goals.
SIB is accelerating a three-pronged upgrade to its manufacturing capabilities as it pivots from traditional metal components to battery structural components for electric vehicles (EVs) and energy storage systems (ESS), leveraging its 40-year design-led manufacturing experience and new industry partnerships.
Design-led manufacturing meets new energy demand
The company, a long-standing supplier to Asian automotive OEMs including Proton and Honda, currently produces brake discs, brake drums, machining brackets, coil springs and stabiliser bars. It is now enhancing precision in automotive components and expanding into battery structural components to serve EV and ESS demand across the region.
“For 40 years we are not only manufacturer but we involved in design development of the component before we start any production. That is our capabilities that we have built up,” Mohd Fahmi Bin Md Isa, Head Of Manufacturing Business.
Three-point plan to penetrate new industries
SIB’s initiative centres on: (1) upgrading precision manufacturing for automotive parts, (2) venturing into new energy components, and (3) producing battery structural components for EVs and ESS. The move responds to shifting industry dynamics and is designed to diversify beyond legacy automotive volumes.
“We are now able to produce battery structural components for batteries to be supplied not only in electric vehicles but also for energy storage systems,” he added.
Collaborations to bridge technology gaps
While the company’s core competence remains metals and component design, SIB is complementing internal capability-building with external collaborations to accelerate its entry into battery structural components and adjacent technologies. The partnership model is intended to shorten learning curves and reduce execution risk as the firm scales into new energy supply chains.
Outcomes and national context
Beyond revenue diversification, SIB expects the initiative to deepen skills among its workforce and contribute to Malaysia’s participation in the global new energy economy tied to ESG priorities. The push into battery structural components positions SIB to align with electrification trends while reinforcing its established role in regional automotive manufacturing.
More stories: NIEC to plug education inclusivity gap for children with diverse needs
About the speaker:
Mohd Fahmi Bin Md Isa
Head Of Manufacturing Business
Sapura Industrial Behad
Encik Mohd Fahmi holds a Bachelor of Science in Mechanical Engineering from Universiti Tenaga Nasional, Malaysia.
Encik Mohd Fahmi began his career as an Engineer at Perodua Manufacturing Sdn. Bhd. in 2002. He has 22 years of experience in the manufacturing industry, producing automotive components and complete vehicles at Perodua with expertise in the areas of Quality Control in Engineering and Inspection, Casting, Machining and Assembly Shops.
He has held several key positions in Perodua Manufacturing Sdn. Bhd. (Deputy General Manager, Quality Control) and Perodua Engine Manufacturing Sdn. Bhd. (Deputy General Manager, Production), within roles responsible for enhancing capability and creating optimal productivity across various production including components of the new KR Engine and KR Turbo Engine Assembly lines.
FAQs:
What is SIB’s core business?
SIB has been in the manufacturing industry for 40 years, primarily producing metal automotive components such as brake discs, brake drums, coil springs, stabilizer bars, and various machining brackets for leading Asian automotive brands.
Which automotive companies does SIB supply to?
SIB supplies components to major automotive manufacturers across Asia, including Proton, Perodua, Honda, and other regional OEMs.
What new industries is SIB venturing into?
SIB is expanding beyond traditional automotive components into the new energy sector, focusing on producing battery structural components for electric vehicles (EVs) and energy storage systems (ESS).
What is unique about SIB’s competitive advantage?
SIB’s strength lies in its 40 years of experience in design and development before production, combined with its expertise in metal-based components and strategic collaborations to adopt new technologies.
What specific new products is SIB developing?
SIB is now capable of manufacturing battery structural components for EV batteries and energy storage systems, in addition to enhancing precision automotive parts.
How is SIB preparing for the shift in manufacturing trends?
The company is implementing a three-pronged strategy: improving precision in automotive components, entering the new energy sector, and collaborating with partners to accelerate technology adoption.
Why is SIB focusing on new energy components?
The move aligns with global ESG priorities and Malaysia’s ambition to participate in the growing new energy industry, ensuring long-term sustainability and competitiveness.
What outcomes does SIB expect from this initiative?
SIB aims to drive revenue growth, enhance workforce capabilities, and contribute to Malaysia’s role in the global new energy economy while maintaining its strong automotive presence.
5W1H summary:
| W/H | Summary |
|---|---|
| What |
1. Pivot to battery structural components. 2. Enhance precision automotive parts. 3. Serve EV, ESS demand across Asia. |
| How |
1. Design-led manufacturing over 40 years. 2. Collaborate with partners for new tech. 3. Upgrade capabilities for new energy. |
| Why |
1. Align with ESG and electrification. 2. Diversify revenue beyond legacy automotive. 3. Build Malaysian workforce capabilities. |
| Who |
1. SIB manufacturing business, Malaysia. 2. Mohd Fahmi Bin Md Isa. 3. Asian automotive OEMs: Proton, Honda. |
| Where |
1. Malaysia manufacturing base. 2. Supplying across Asia, ASEAN. 3. New energy components for region. |
| When |
1. 40-year track record. 2. Capability expansion happening now. 3. Near-term penetration into new industries. |

